Java动态代理
Java动态代理的方式有两种:
- JDK动态代理
- CGLib动态代理
spring aop
aop基本概念
-
Aspect:切面类
-
Join point:是在应用执行过程中能够插入切面的一个点。这个点可以是调用方法时、抛出异常时、甚至修改一个字段时。切面代码可以利用这些点插入到应用的正常流程之中,并添加新的行为。
-
Advice:切入前后执行的建议
- before:方法执行之前执行
- after:方法执行之后执行
- after-returning:仅在方法成功完成时,在方法执行后执行
- after-throwing:仅在方法通过抛出异常退出时,才在方法执行后执行
- around:在调用方法之前和之后执行,是before、after的组合
-
PointCut:一个切面并不需要通知应用的所有连接点。切点有助于缩小切面所通知的连接点范围。切点的定义会匹配通知所要织入的一个或多个连接点。我们通常使用明确的类和方法名称,或是利用正则表达式定义所匹配的类和方法名称来指定这些切点。另外,有些AOP框架是允许我们创建动态的切点,可以根据运行时的决策(比如方法的参数值)来决定是否应用通知。
【PointCut的表达式】
- 方法标签匹配方式
假设定义了EmployeeManager接口。
1) execution(* com.howtodoinjava.EmployeeManager.*(..))
以上切入点表达式可以匹配EmployeeManger接口中所有的方法。
2)
当切面方法和EmployeeManager接口在相同的包内,如果切入点表达式匹配所有所有方法,则表达式可以改成:
execution(* EmployeeManager.*(..))
3) 匹配EmployeeManager接口的所有public方法。
execution(public * EmployeeManager.*(..))
4) 匹配EmployeeManager接口中权限为public并返回类型为EmployeeDTO的所有方法。
execution(public EmployeeDTO EmployeeManager.*(..))
5) 匹配EmployeeManager接口中权限为public并返回类型为EmployeeDTO,第一个参数为EmployeeDTO类型的所有方法。
execution(public EmployeeDTO EmployeeManager.*(EmployeeDTO, ..))
6) 匹配EmployeeManager接口中权限为public、返回类型为EmployeeDTO,参数明确定义为EmployeeDTO,Integer的所有方法。 execution(public EmployeeDTO EmployeeManager.*(EmployeeDTO, Integer))
- 类型标签匹配模式
1) 匹配在com.howtodoinjava包下所有类型中所有的方法
within(com.howtodoinjava.*)
2) 匹配在com.howtodoinjava包以及其子包下所有类型中所有的方法
within(com.howtodoinjava..*)
3) 匹配其他包一个类下的所有方法
within(com.howtodoinjava.EmployeeManagerImpl)
4) 匹配同一个包下一个类下的所有方法
within(EmployeeManagerImpl)
5) 匹配一个接口下的所有继承者的所有方法
within(EmployeeManagerImpl+)
- bean名字匹配模式
匹配所有以Manager结尾的beans中的所有方法
bean(*Manager)
- 切入点表达式拼接
在AspectJ中,切入点表达式可以通过&&, ,!等操作符进行拼接 bean(*Manager) bean(*DAO) -
Introduction:给原有的类引入新的接口功能,参考示例
-
Target object:切入的目标对象
-
Weaving:织入,将切面应用到目标对象从而创建一个新的代理对象的过程,这个过程可以发生在编译期、类装载期及运行期。
spring aop的实现方式
1. xml方式(ProxyFactoryBean)
定义一个业务服务类:
public class CustomerService {
private String name;
private String url;
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void setUrl(String url) {
this.url = url;
}
public void printName() {
System.out.println("Customer name : " + this.name);
}
public void printURL() {
System.out.println("Customer website : " + this.url);
}
public void printThrowException() {
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
}
}
定义切面类,在业务类方法执行前后做一些事情
public class CustomerInterceptor implements MethodInterceptor {
@Override
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation methodInvocation) throws Throwable {
try {
System.out.println("方法调用之前做一些事情....");
Object result = methodInvocation.proceed();
System.out.println("方法调用之后做一些事情");
return result;
}catch (Exception ex){
System.out.println("执行方法抛出异常");
throw ex;
}
}
}
public class MyBeforeAdvice implements MethodBeforeAdvice {
@Override
public void before(Method method, Object[] objects, @Nullable Object o) throws Throwable{
System.out.println(o.getClass() + ":"+method.getName()+" 方法准备执行");
}
}
public class MyAfterAdvice implements AfterReturningAdvice {
@Override
public void afterReturning(Object returnValue, Method method, Object[] args, Object target) throws Throwable {
System.out.println(target.getClass()+":"+method.getName()+" 方法执行完成,返回结果:"+returnValue);
}
}
XML配置
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<!--示例1:拦截所有方法-->
<bean id="customerService" class="com.qigang.spring_aop.CustomerService">
<property name="name" value="nameeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeee"/>
<property name="url" value="urlllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllll"/>
</bean>
<bean id="customerInterceptor" class="com.qigang.spring_aop.CustomerInterceptor"></bean>
<bean id="beforeAdvice" class="com.qigang.spring_aop.MyBeforeAdvice"></bean>
<bean id="afterAdvice" class="com.qigang.spring_aop.MyAfterAdvice"></bean>
<bean id="customerServiceProxy" class="org.springframework.aop.framework.ProxyFactoryBean">
<property name="target" ref="customerService"></property>
<property name="interceptorNames">
<list>
<value>customerInterceptor</value>
<value>beforeAdvice</value>
<value>afterAdvice</value>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
<!--示例2:拦截pointcut中指定的方法-->
<!--<bean id="customerService" class="com.qigang.spring_aop.CustomerService">
<property name="name" value="nameeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeee"/>
<property name="url" value="urlllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllllll"/>
</bean>
<bean id="customerInterceptor" class="com.qigang.spring_aop.CustomerInterceptor"></bean>
<bean id="beforeAdvice" class="com.qigang.spring_aop.MyBeforeAdvice"></bean>
<bean id="afterAdvice" class="com.qigang.spring_aop.MyAfterAdvice"></bean>
<bean id="customerServiceProxy" class="org.springframework.aop.framework.ProxyFactoryBean">
<property name="target" ref="customerService"></property>
<property name="interceptorNames">
<list>
<value>customerAdvisor</value>
<value>beforeAdvice</value>
<value>afterAdvice</value>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
<bean id="customerPointcut" class="org.springframework.aop.support.NameMatchMethodPointcut">
<property name="mappedName" value="printName"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="customerAdvisor" class="org.springframework.aop.support.DefaultPointcutAdvisor">
<property name="advice" ref="customerInterceptor"></property>
<property name="pointcut" ref="customerPointcut"></property>
</bean>-->
</beans>
测试方法
ApplicationContext appContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
CustomerService cust = (CustomerService) appContext.getBean("customerServiceProxy");
cust.printName();
cust.printURL();
try {
cust.printThrowException();
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("出现异常了...");
}
2. 代码方式(ProxyFactory)
利用代码方式可以实现上面一样的功能
ProxyFactory proxyFactory = new ProxyFactory();
NameMatchMethodPointcut pointcut=new NameMatchMethodPointcut();
pointcut.setMappedName("*");
proxyFactory.addAdvisor(new DefaultPointcutAdvisor(pointcut, new CustomerInterceptor()));
proxyFactory.addAdvisor(new DefaultPointcutAdvisor(pointcut, new MyBeforeAdvice()));
proxyFactory.addAdvisor(new DefaultPointcutAdvisor(pointcut, new MyAfterAdvice()));
proxyFactory.setTarget(new CustomerService());
CustomerService cust = (CustomerService)proxyFactory.getProxy();
cust.printName();
cust.printURL();
try {
cust.printThrowException();
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("出现异常了...");
}
spring中advisor的种类:
* DefaultPointcutAdvisor,配合NameMatchMethodPointcut可以根据名称来匹配需要进行AOP处理的方法,限定在某一个类中的某一些方法
* RegexpMethodPointcutAdvisor,通过正则表达式来对某些类中的某些方法进行AOP处理,范围更广更灵活
3. 自动代理
上面两种方式都是指定了target来进行AOP处理,正常情况不可能每个对象需要AOP处理的时候都设置target单独写一份代码,最好是能针对指定规则的类或者方法进行统一的AOP处理,使用正则表达式来进行灵活规则匹配。
示例中还是使用上方的CustomerService、CustomerInterceptor,使用统一的正则表达式配置来使用CustomerInterceptor对CustomerService进行AOP功能增强。只需要在配置文件中配置autoproxy即可。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--被代理对象-->
<bean id="customerService" class="com.qigang.spring_aop.CustomerService"></bean>
<!--advice-->
<bean id="customerInterceptor" class="com.qigang.spring_aop.CustomerInterceptor"></bean>
<!--advisor-->
<bean id="regexpAdvisor" class="org.springframework.aop.support.RegexpMethodPointcutAdvisor">
<property name="advice" ref="customerInterceptor"></property>
<!-- 切入点正则表达式 -->
<property name="pattern" value="com.qigang.spring_aop.*"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 自动扫描切面代理类 -->
<bean class="org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy.DefaultAdvisorAutoProxyCreator">
<property name="optimize" value="true"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
ApplicationContext appContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("autoproxy.xml");
CustomerService cust = (CustomerService) appContext.getBean("customerService");
cust.printName();
cust.printURL();
try {
cust.printThrowException();
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("出现异常了...");
}
DefaultAdvisorAutoProxyCreator
autoproxy的核心是DefaultAdvisorAutoProxyCreator,另外还有一个BeanNameAutoProxyCreator,以及后面将要介绍的AspectJAwareAdvisorAutoProxyCreator等。
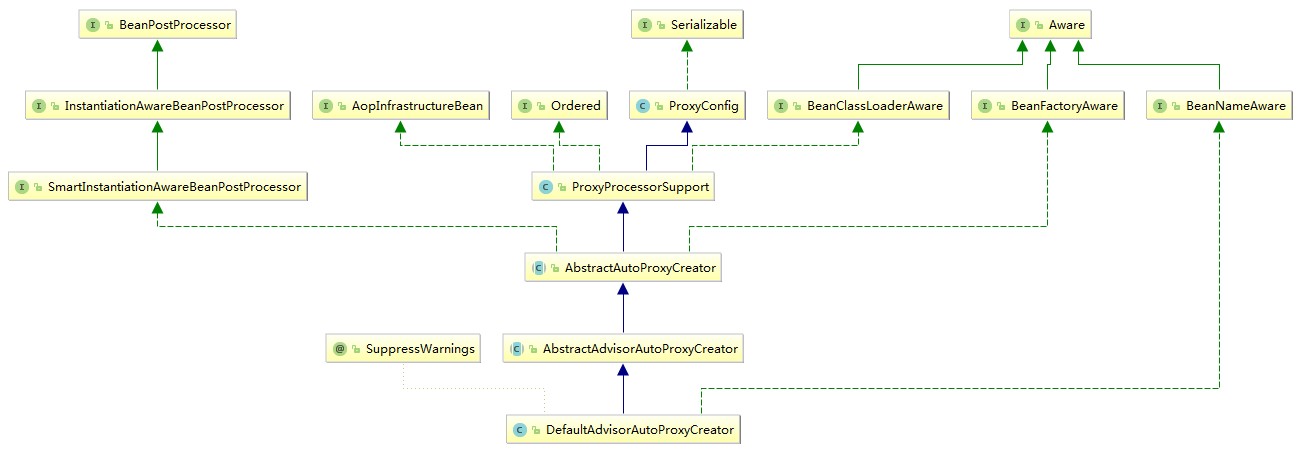
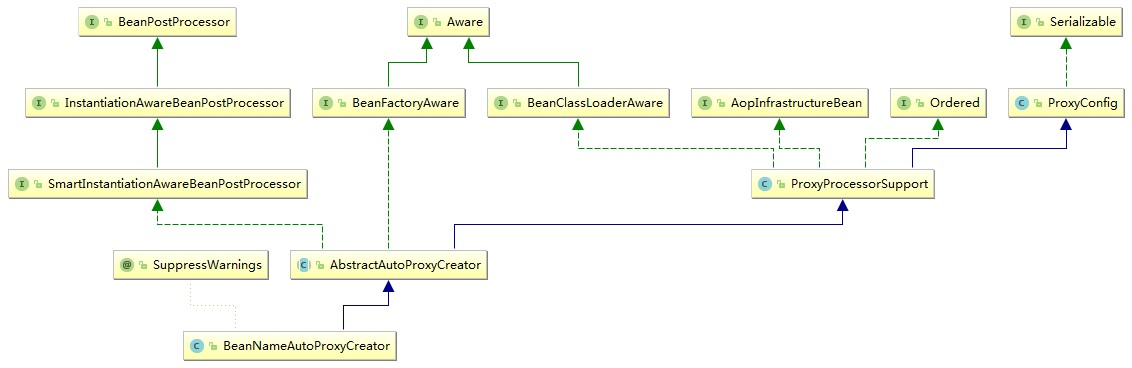
这几个类都继承了AbstractAutoProxyCreator>SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor>InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor>BeanPostProcessor。
BeanPostProcessor的主要方法:
BeanPostProcessor
postProcessBeforeInitialization 初始化前扩展(执行init-method前)
postProcessAfterInitialization 初始化后扩展(执行init-method后)
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor
postProcessBeforeInstantiation 对象实例化前扩展
postProcessAfterInstantiation 对象实例化后扩展
postProcessPropertyValues 属性依赖注入前扩展
SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor
predictBeanType 预测bean的类型,在beanFactory的getType时被调用
determineCandidateConstructors 对象实例化时决定要使用的构造函数时被调用
getEarlyBeanReference 循环依赖处理时获取Early对象引用时被调用
自动代理最核心的逻辑都在实例化前AbstractAutoProxyCreator.postProcessBeforeInstantiation以及初始化后AbstractAutoProxyCreator.postProcessAfterInitialization这两个方法中。
-
AbstractAutoProxyCreator.postProcessBeforeInstantiation
这个方法中主要逻辑在
getCustomTargetSource以及createProxy中,只有当配置了自定义的customTargetSourceCreators的时候才会直接创建代理对象,一般情况下不会自定义TargetSourceCreator(参考TargetSource目标源)。 -
AbstractAutoProxyCreator.postProcessAfterInitialization
这个方法主要逻辑在
wrapIfNecessary>getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean>createProxy,getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean是个抽象方法,如果使用的DefaultAdvisorProxyCreator,那具体实现在其抽象父类AbstractAdvisorAutoProxyCreator中,调试进入到createProxy方法中可以看到,在获取到合适的advisors之后,最终还是通过ProxyFactory来创建目标对象的代理,而ProxyFactory内部在上面的章节分析中可以看出来最终还是通过JDK动态代理或者CGLib动态代理来创建代理对象的,也就是JDKDynamicAopProxy和ObjenesisCglibAopProxy
BeanNameAutoProxyCreator
同DefaultAdvisorAutoProxyCreator类似,示例xml配置
<bean class="org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy.BeanNameAutoProxyCreator">
<property name="beanNames">
<value>*Service</value>
</property>
<property name="interceptorNames">
<list>
<value>customerInterceptor</value>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator
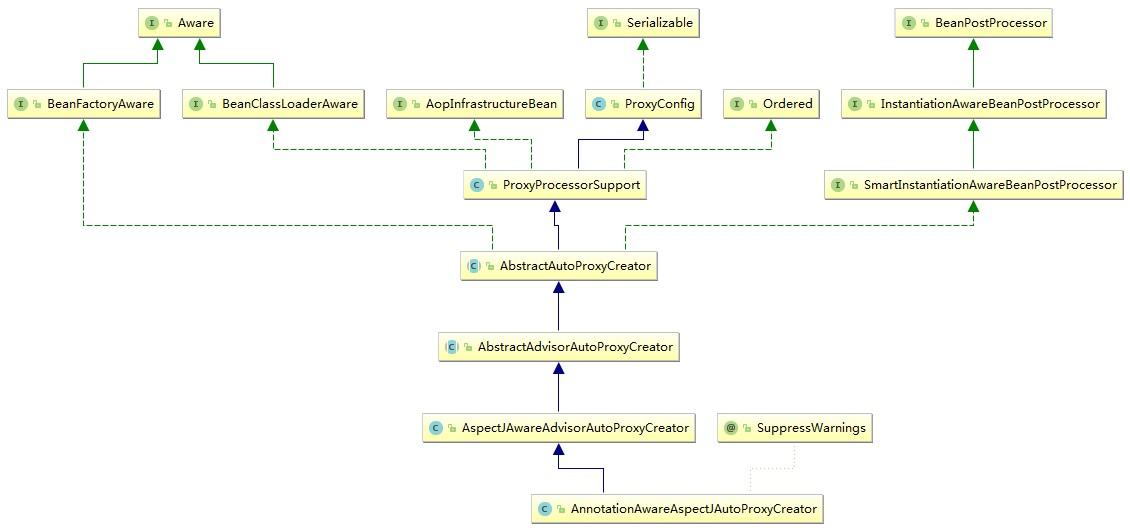
AspectJAwareAdvisorAutoProxyCreator用于xml配置版的AspectJ切面自动代理创建(<aop:config/>)
AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator用于基于注解的自动代理创建(<aop:aspectj-autoproxy/> 或 @EnableAspectJAutoProxy),下面对这个自动代理类进行较为详细的示例说明。
4. aspectj
aspectj+xml
public class Logging {
public void beforeAdvice() {
System.out.println("beforeAdvice");
}
public void afterAdvice() {
System.out.println("afterAdvice");
}
public void afterReturningAdvice(Object retVal){
System.out.println("afterReturningAdvice:" + retVal.toString() );
}
public void AfterThrowingAdvice(IllegalArgumentException ex) {
System.out.println("exception: " + ex.toString());
}
}
public class Student {
private Integer age;
private String name;
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public Integer getAge() {
System.out.println("Age : " + age );
return age;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
System.out.println("Name : " + name );
return name;
}
public void printThrowException(){
System.out.println("Exception raised");
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
}
}
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("aspectj.xml");
Student student = (Student) context.getBean("student");
student.getName();
student.getAge();
student.printThrowException();
xml配置文件内容:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<aop:config>
<aop:aspect id = "log" ref = "logging">
<aop:pointcut id = "allMethods" expression = "execution(* com.qigang.aspectj.*.*(..))"/>
<aop:before pointcut-ref = "allMethods" method = "beforeAdvice"/>
<aop:after pointcut-ref = "allMethods" method = "afterAdvice"/>
<aop:after-returning pointcut-ref = "allMethods" returning = "retVal" method = "afterReturningAdvice"/>
<aop:after-throwing pointcut-ref = "allMethods" throwing = "ex" method = "AfterThrowingAdvice"/>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
<bean id = "student" class = "com.qigang.aspectj.Student">
<property name = "name" value = "Zara" />
<property name = "age" value = "11"/>
</bean>
<bean id = "logging" class = "com.qigang.aspectj.Logging"/>
</beans>
aspectj+annotation
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Aspect
@Component
public class Logging2 {
@Pointcut("execution(* com.qigang.aspectj.*.*(..))")
public void allMethods(){}
@Before("allMethods()")
public void beforeAdvice() {
System.out.println("beforeAdvice");
}
@After("allMethods()")
public void afterAdvice() {
System.out.println("afterAdvice");
}
@AfterReturning(pointcut = "allMethods()", returning = "retVal")
public void afterReturningAdvice(Object retVal){
System.out.println("afterReturningAdvice:" + retVal );
}
@AfterThrowing(pointcut = "allMethods()", throwing = "ex")
public void AfterThrowingAdvice(IllegalArgumentException ex) {
System.out.println("exception: " + ex.toString());
}
}
@Component("student")
public class Student {
//...
}
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("aspectj.xml");
Student student = (Student) context.getBean("student");
student.getName();
student.getAge();
student.printThrowException();
xml配置文件内容只保留两行
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<!--测试AspectJ-->
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy/>
<context:component-scan base-package="com.qigang.aspectj"/>
</beans>
如果完全去除xml配置文件的话,应用中使用@EnableAspectJAutoProxy注解即可
@Component
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "com.qigang.aspectj")
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(Test.class);
Student student = (Student) applicationContext.getBean("student");
student.getName();
student.getAge();
student.printThrowException();
}
}
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy原理
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Import(AspectJAutoProxyRegistrar.class)
public @interface EnableAspectJAutoProxy {
/**
* Indicate whether subclass-based (CGLIB) proxies are to be created as opposed
* to standard Java interface-based proxies. The default is {@code false}.
*/
boolean proxyTargetClass() default false;
/**
* Indicate that the proxy should be exposed by the AOP framework as a {@code ThreadLocal}
* for retrieval via the {@link org.springframework.aop.framework.AopContext} class.
* Off by default, i.e. no guarantees that {@code AopContext} access will work.
* @since 4.3.1
*/
boolean exposeProxy() default false;
}
核心就是@Import(AspectJAutoProxyRegistrar.class),AspectJAutoProxyRegistrar这个类实现了ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar,在registerBeanDefinitions()这个实现方法里面通过AopConfigUtils向容器里面注册了AspectJAnnotationAutoProxyCreator的子类AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator,在上面已经介绍过,这个类实现了SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor,在最主要的实例化前方法AbstractAutoProxyCreator.postProcessBeforeInstantiation()和AbstractAutoProxyCreator.postProcessAfterInitialization()中通过动态代理来生成代理类。
AbstractAutoProxyCreator.postProcessBeforeInstantiation()
AbstractAutoProxyCreator.createProxy()
//**************************************************************************************
protected Object createProxy(Class<?> beanClass, @Nullable String beanName,
@Nullable Object[] specificInterceptors, TargetSource targetSource) {
if (this.beanFactory instanceof ConfigurableListableBeanFactory) {
AutoProxyUtils.exposeTargetClass((ConfigurableListableBeanFactory) this.beanFactory, beanName, beanClass);
}
ProxyFactory proxyFactory = new ProxyFactory();
proxyFactory.copyFrom(this);
if (!proxyFactory.isProxyTargetClass()) {
if (shouldProxyTargetClass(beanClass, beanName)) {
proxyFactory.setProxyTargetClass(true);
}
else {
evaluateProxyInterfaces(beanClass, proxyFactory);
}
}
Advisor[] advisors = buildAdvisors(beanName, specificInterceptors);
proxyFactory.addAdvisors(advisors);
proxyFactory.setTargetSource(targetSource);
customizeProxyFactory(proxyFactory);
proxyFactory.setFrozen(this.freezeProxy);
if (advisorsPreFiltered()) {
proxyFactory.setPreFiltered(true);
}
return proxyFactory.getProxy(getProxyClassLoader());
}
//**************************************************************************************
可以看到它的底层其实就是ProxyFactory.getProxy()方法。
源码解析
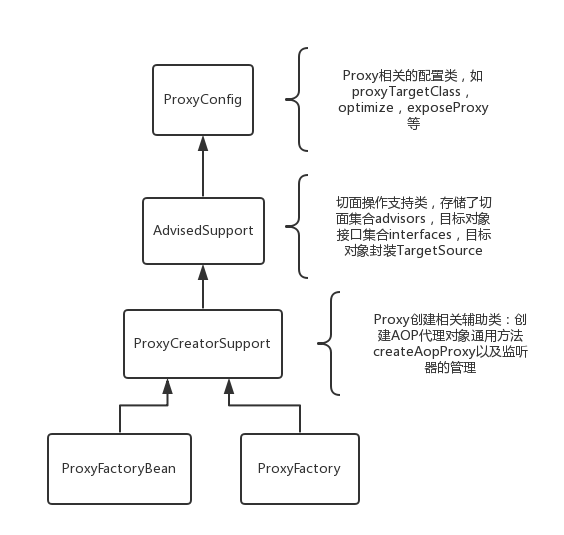
ProxyFactoryBean
xml配置文件中配置的代理类的类型是org.springframework.aop.framework.ProxyFactoryBean,是一个FactoryBean,可以猜测到代理类的生成逻辑都在getObject()方法里面。
ProxyFactoryBean.getObject();
//getObject()第一行代码就是初始化advisor链,也就是xml配置文件中interceptorNames列表里面的对象
initializeAdvisorChain();
//默认是singleton
getSingletonInstance();
getProxy(createAopProxy());
ProxyCreatorSupport.createAopProxy();
getAopProxyFactory().createAopProxy(this);
DefaultAopProxyFactory.createAopProxy();
//********************************************************************************
@Override
public AopProxy createAopProxy(AdvisedSupport config) throws AopConfigException {
if (config.isOptimize() || config.isProxyTargetClass() || hasNoUserSuppliedProxyInterfaces(config)) {
Class<?> targetClass = config.getTargetClass();
if (targetClass == null) {
throw new AopConfigException("TargetSource cannot determine target class: " +
"Either an interface or a target is required for proxy creation.");
}
if (targetClass.isInterface() || Proxy.isProxyClass(targetClass)) {
return new JdkDynamicAopProxy(config);
}
return new ObjenesisCglibAopProxy(config);
}
else {
return new JdkDynamicAopProxy(config);
}
}
//********************************************************************************
如果被代理的目标类实现了一个或多个自定义的接口,那么就会使用 JDK 动态代理,如果没有实现任何接口,会使用 CGLIB 实现代理,如果设置了 proxy-target-class=“true”,那么通常都会使用 CGLIB。
回到ProxyFactoryBean.getProxy()方法
ProxyFactoryBean.getProxy();
//假如使用JDK动态代理,JdkDynamicAopProxy实现InvocationHandler,所以具体生成代理类的逻辑在invoke()方法中
JdkDynamicAopProxy.getProxy();
Proxy.newProxyInstance(classLoader, proxiedInterfaces, this);
//假如使用CGLib动态代理,执行CglibAopProxy.getProxy方法
ObjenesisCglibAopProxy.getProxy();
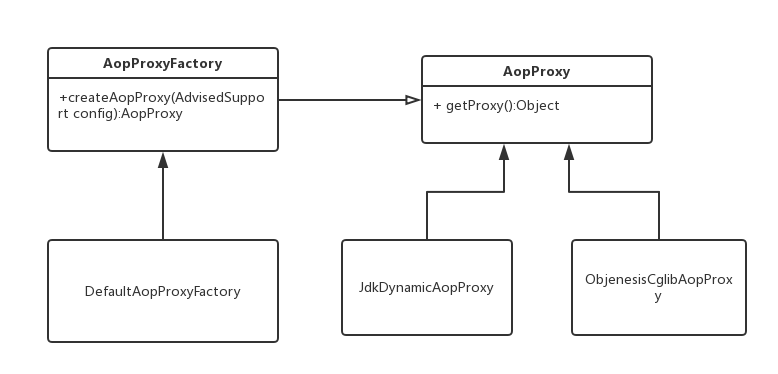
JdkDynamicAopProxy
如果被代理的类实现了某个接口,就会使用JdkDynamicAopProxy代理,执行invoke方法
final class JdkDynamicAopProxy implements AopProxy, InvocationHandler, Serializable{}
invoke();
//**************************************************************************************************
// Get the interception chain for this method.
//【核心方法】获取interceptor和advice链
List<Object> chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, targetClass);
// Check whether we have any advice. If we don't, we can fallback on direct
// reflective invocation of the target, and avoid creating a MethodInvocation.
if (chain.isEmpty()) {
// We can skip creating a MethodInvocation: just invoke the target directly
// Note that the final invoker must be an InvokerInterceptor so we know it does
// nothing but a reflective operation on the target, and no hot swapping or fancy proxying.
Object[] argsToUse = AopProxyUtils.adaptArgumentsIfNecessary(method, args);
retVal = AopUtils.invokeJoinpointUsingReflection(target, method, argsToUse);
}
else {
// We need to create a method invocation...
invocation = new ReflectiveMethodInvocation(proxy, target, method, args, targetClass, chain);
// Proceed to the joinpoint through the interceptor chain.
//【核心方法】实际调用,这里会调用实际的interceptor或者advice类的方法,在上方的[xml方式(ProxyFactoryBean)]示例中就是CustomerInterceptor、MyBeforeAdvice、MyAfterAdvice这三个类
retVal = invocation.proceed();
}
//**************************************************************************************************
ObjenesisCglibAopProxy
class ObjenesisCglibAopProxy extends CglibAopProxy{}
getProxy();
//【核心方法】,在获取回调方法的时候创建了DynamicAdvisedInterceptor对象,这个对象的核心方法是invoke()方法
getCallbacks();
Callback aopInterceptor = new DynamicAdvisedInterceptor(this.advised);
//跟JdkDynamicAopProxy.invoke方法类似,里面获取了advice链,逐个执行里面的方法
DynamicAdvisedInterceptor.invoke();
//**************************************************************************************************
List<Object> chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, targetClass);
Object retVal;
// Check whether we only have one InvokerInterceptor: that is,
// no real advice, but just reflective invocation of the target.
if (chain.isEmpty() && Modifier.isPublic(method.getModifiers())) {
// We can skip creating a MethodInvocation: just invoke the target directly.
// Note that the final invoker must be an InvokerInterceptor, so we know
// it does nothing but a reflective operation on the target, and no hot
// swapping or fancy proxying.
Object[] argsToUse = AopProxyUtils.adaptArgumentsIfNecessary(method, args);
retVal = methodProxy.invoke(target, argsToUse);
}
else {
// We need to create a method invocation...
retVal = new CglibMethodInvocation(proxy, target, method, args, targetClass, chain, methodProxy).proceed();
}
//**************************************************************************************************
ProxyFactory
核心逻辑都在ProxyFactory.getProxy()方法中,底层其实跟ProxyFactoryBean是一样的
参考
Spring源码-AOP(六)-自动代理与DefaultAdvisorAutoProxyCreator
Spring AOP的核心类:AbstractAdvisorAutoProxy自动代理创建器深度剖析(AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator)