总结zk知识点
一、安装配置
1. 下载解压
tar -zxvf zookeeper-3.4.13.tar.gz
2. 配置
- copy示例配置文件
cd conf
cp zoo_sample.cfg zoo.cfg
- 设置环境变量
vim /etc/profile
export ZOOKEEPER_HOME=/root/zookeeper/zookeeper-3.4.13
export PATH=.:$PATH:$ZOOKEEPER_HOME/bin
. /etc/profile
- 配置伪集群环境
1. 单台机器上创建3个不同的配置文件zoo1.cfg、zoo2.cfg、zoo3.cfg, 配置内容见下方。
2. 在配置文件指定的dataDir目录下面创建myid文件,内容分别为0,1,2,对应配置文件中的server.X
3. 分别创建dataDir/dataLogDir指定的目录
4. 启动3个服务:
sh ./bin/zkServer.sh start ./conf/zoo1.cfg
sh ./bin/zkServer.sh start ./conf/zoo2.cfg
sh ./bin/zkServer.sh start ./conf/zoo3.cfg
5. 查看3个服务的状态:
sh ./bin/zkServer.sh status ./conf/zoo1.cfg
sh ./bin/zkServer.sh status ./conf/zoo2.cfg
sh ./bin/zkServer.sh status ./conf/zoo3.cfg
# zoo1.cfg
# The number of milliseconds of each tick
tickTime=2000
# The number of ticks that the initial
# synchronization phase can take
initLimit=10
# The number of ticks that can pass between
# sending a request and getting an acknowledgement
syncLimit=5
# the directory where the snapshot is stored.
# do not use /tmp for storage, /tmp here is just
# example sakes.
dataDir=/usr/local/zk/data_1
# the port at which the clients will connect
clientPort=2181
# the maximum number of client connections.
# increase this if you need to handle more clients
#maxClientCnxns=60
#
# Be sure to read the maintenance section of the
# administrator guide before turning on autopurge.
#
# http://zookeeper.apache.org/doc/current/zookeeperAdmin.html#sc_maintenance
#
# The number of snapshots to retain in dataDir
# 保留多少个快照
autopurge.snapRetainCount=3
# Purge task interval in hours
# Set to "0" to disable auto purge feature
# 日志多少个小时清理一次
autopurge.purgeInterval=1
dataLogDir=/usr/local/zk/logs_1
server.0=localhost:2287:3387
server.1=localhost:2288:3388
server.2=localhost:2289:3389
# zoo2.cfg
# The number of milliseconds of each tick
tickTime=2000
# The number of ticks that the initial
# synchronization phase can take
initLimit=10
# The number of ticks that can pass between
# sending a request and getting an acknowledgement
syncLimit=5
# the directory where the snapshot is stored.
# do not use /tmp for storage, /tmp here is just
# example sakes.
dataDir=/usr/local/zk/data_2
# the port at which the clients will connect
clientPort=2182
# the maximum number of client connections.
# increase this if you need to handle more clients
#maxClientCnxns=60
#
# Be sure to read the maintenance section of the
# administrator guide before turning on autopurge.
#
# http://zookeeper.apache.org/doc/current/zookeeperAdmin.html#sc_maintenance
#
# The number of snapshots to retain in dataDir
#autopurge.snapRetainCount=3
# Purge task interval in hours
# Set to "0" to disable auto purge feature
#autopurge.purgeInterval=1
dataLogDir=/usr/local/zk/logs_2
server.0=localhost:2287:3387
server.1=localhost:2288:3388
server.2=localhost:2289:3389
# zoo3.cfg
# The number of milliseconds of each tick
tickTime=2000
# The number of ticks that the initial
# synchronization phase can take
initLimit=10
# The number of ticks that can pass between
# sending a request and getting an acknowledgement
syncLimit=5
# the directory where the snapshot is stored.
# do not use /tmp for storage, /tmp here is just
# example sakes.
dataDir=/usr/local/zk/data_3
# the port at which the clients will connect
clientPort=2183
# the maximum number of client connections.
# increase this if you need to handle more clients
#maxClientCnxns=60
#
# Be sure to read the maintenance section of the
# administrator guide before turning on autopurge.
#
# http://zookeeper.apache.org/doc/current/zookeeperAdmin.html#sc_maintenance
#
# The number of snapshots to retain in dataDir
#autopurge.snapRetainCount=3
# Purge task interval in hours
# Set to "0" to disable auto purge feature
#autopurge.purgeInterval=1
dataLogDir=/usr/local/zk/logs_3
server.0=localhost:2287:3387
server.1=localhost:2288:3388
server.2=localhost:2289:3389
3. 启动zk服务、自带客户端使用
- 启动/停止zk服务,查看zk服务状态
sh ./bin/zkServer.sh start
sh ./bin/zkServer.sh stop
# 可以查看状态,看是leader节点还是follower节点
sh ./bin/zkServer.sh status
- 自带客户端使用
zkCli.sh -server localhost:2181
create /zk myData
ls /
get /zk
set /zk myData1
delete /zk
#强制删除节点,即使节点下有子节点
rmr /dubbo
客户端操作命令
| 命令 | 说明 | 参数 |
|---|---|---|
create [-s] [-e] path data acl |
创建Znode | -s 指定是顺序节点,node名称后面会有一串数字 -e 指定是临时节点,会话消失后也跟着消失 |
ls path [watch] |
列出Path下所有子Znode | |
get path [watch] |
获取Path对应的Znode的数据和属性 | |
ls2 path [watch] |
查看Path下所有子Znode以及子Znode的属性 | |
set path data [version] |
更新节点 | version 数据版本 |
delete path [version] |
删除节点, 如果要删除的节点有子Znode则无法删除 | version 数据版本 |
rmr path |
删除节点, 如果有子Znode则递归删除 | |
setquota -n|-b val path |
修改Znode配额 | -n 设置子节点最大个数 -b 设置节点数据最大长度 |
history |
列出历史记录 |
1:创建普通节点
create /app1 hello
只有永久节点下面可以创建子节点,临时节点无法创建子节点
2: 创建顺序节点
create -s /app3 world
3:创建临时节点
create -e /tempnode world
4:创建顺序的临时节点
create -s -e /tempnode2 aaa
5:获取节点数据
get /app1
6:修改节点数据
set /app1 xxx
7:删除节点
delete /app1 删除的节点不能有子节点
rmr /app1 递归删除
二、概念
节点类型
- 临时节点
- 永久节点
- 临时节点(带序列)
- 永久节点(带序列)
zookeeper会话
客户端和服务端建立连接后,会话随之建立,生成一个全局唯一的会话ID(Session ID)。服务器和客户端之间维持的是一个长连接,在SESSION_TIMEOUT时间内,服务器会确定客户端是否正常连接(客户端会定时向服务器发送heart_beat,服务器重置下次SESSION_TIMEOUT时间)。因此,在正常情况下,Session一直有效,并且ZK集群所有机器上都保存这个Session信息。 zookeeper服务端配置文件zoo.cfg中可以配置两个个参数来设置会话超时时间范围,在创建客户端ZkClient的时候都可以指定会话超时时间,但是这个时间必须在服务器zoo.cfg中配置的超时时间范围内,会话超时之后,会话中创建的临时节点、watcher都会被删除。
#zoo.cfg会话超时时间范围配置
#默认情况下zoo.cfg中的配置ticktime=2000,单位是ms
#minSessionTimeout默认值=2*ticktime
#maxSessionTimeout默认值=20*ticktime
minSessionTimeout=2000
maxSessionTimeout=5000
ZkClient创建客户端的参数:
zkServer, zookeeper服务器地址,用逗号分隔
sessionTimeout,会话超时时间,单位毫秒,默认为30000ms
connectionTimeout,连接超时时间
IZkConnection,连接的实现类
zkSerializer,自定义序列化实现
zk的watch机制
zk客户端向zk服务器注册watcher的同时,会将watcher对象存储在客户端的watchManager。zk服务器触发watcher事件后,会向客户端发送通知,客户端线程从watchManager中回调watcher执行相应的功能。
watcher只能监听子节点,不能监听到孙节点。watcher设置后,一旦触发一次后就会失效,如果要想一直监听,需要在process回调函数里重新注册相同的 watcher
- 通知类似于数据库中的触发器, 对某个Znode设置
Watcher, 当Znode发生变化的时候,WatchManager会调用对应的Watcher - 当Znode发生删除, 修改, 创建, 子节点修改的时候, 对应的
Watcher会得到通知 Watcher的特点- 一次性触发 一个
Watcher只会被触发一次, 如果需要继续监听, 则需要再次添加Watcher - 事件封装:
Watcher得到的事件是被封装过的, 包括三个内容keeperState, eventType, path
- 一次性触发 一个
| KeeperState | EventType | 触发条件 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|---|
| None | 连接成功 | ||
| SyncConnected | NodeCreated | Znode被创建 | 此时处于连接状态 |
| SyncConnected | NodeDeleted | Znode被删除 | 此时处于连接状态 |
| SyncConnected | NodeDataChanged | Znode数据被改变 | 此时处于连接状态 |
| SyncConnected | NodeChildChanged | Znode的子Znode数据被改变 | 此时处于连接状态 |
| Disconnected | None | 客户端和服务端断开连接 | 此时客户端和服务器处于断开连接状态 |
| Expired | None | 会话超时 | 会收到一个SessionExpiredException |
| AuthFailed | None | 权限验证失败 | 会收到一个AuthFailedException |
ACL权限控制
ZAB协议
zk的leader选举机制
Leader选举是保证分布式数据一致性的关键所在。当Zookeeper集群中的一台服务器出现以下两种情况之一时,需要进入Leader选举。
- 服务器启动时期的Leader选举
若进行Leader选举,则至少需要两台机器,这里选取3台机器组成的服务器集群为例。在集群初始化阶段,当有一台服务器Server1启动时,其单独无法进行和完成Leader选举,当第二台服务器Server2启动时,此时两台机器可以相互通信,每台机器都试图找到Leader,于是进入Leader选举过程。选举过程如下
(1) 每个Server发出一个投票。由于是初始情况,Server1和Server2都会将自己作为Leader服务器来进行投票,每次投票会包含所推举的服务器的myid和ZXID,使用(myid, ZXID)来表示,此时Server1的投票为(1, 0),Server2的投票为(2, 0),然后各自将这个投票发给集群中其他机器。
(2) 接受来自各个服务器的投票。集群的每个服务器收到投票后,首先判断该投票的有效性,如检查是否是本轮投票、是否来自LOOKING状态的服务器。
(3) 处理投票。针对每一个投票,服务器都需要将别人的投票和自己的投票进行PK,PK规则如下
· 优先检查ZXID。ZXID比较大的服务器优先作为Leader。
· 如果ZXID相同,那么就比较myid。myid较大的服务器作为Leader服务器。
对于Server1而言,它的投票是(1, 0),接收Server2的投票为(2, 0),首先会比较两者的ZXID,均为0,再比较myid,此时Server2的myid最大,于是更新自己的投票为(2, 0),然后重新投票,对于Server2而言,其无须更新自己的投票,只是再次向集群中所有机器发出上一次投票信息即可。
(4) 统计投票。每次投票后,服务器都会统计投票信息,判断是否已经有过半机器接受到相同的投票信息,对于Server1、Server2而言,都统计出集群中已经有两台机器接受了(2, 0)的投票信息,此时便认为已经选出了Leader。
(5) 改变服务器状态。一旦确定了Leader,每个服务器就会更新自己的状态,如果是Follower,那么就变更为FOLLOWING,如果是Leader,就变更为LEADING。
- 服务器运行时期的Leader选举
在Zookeeper运行期间,Leader与非Leader服务器各司其职,即便当有非Leader服务器宕机或新加入,此时也不会影响Leader,但是一旦Leader服务器挂了,那么整个集群将暂停对外服务,进入新一轮Leader选举,其过程和启动时期的Leader选举过程基本一致过程相同。
三、zookeeper的应用场景
数据发布、订阅
watcher机制,数据的推拉结合,配置中心的功能就是基于这个来实现的
命名服务
分布式协调、通知
借助watcher机制,不同的客户端对同一个节点进行watcher注册,监听数据节点的变化(节点本身或者子节点),客户端收到变化通知之后可以做相应处理
- 心跳检测
- 工作进度汇报
- 系统调度,任务进度数据实时感知
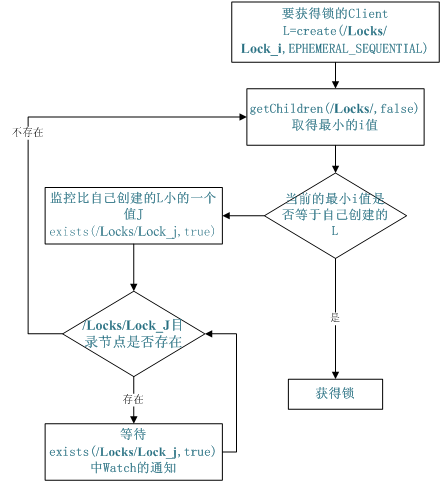
分布式锁
- 排它锁(写锁)
获取锁的方式就是在/exclusive_lock/lock(这个是示例节点名称)下创建临时子节点,其它客户端无法创建相同名称的节点,当获取锁的客户端处理完成或者宕机,临时节点删除,其它节点监听到删除事件就去重新创建节点获取锁
- 共享锁(读锁)
若事务T1对数据对象O1加上共享锁,那么当前事务只能对O1进行读取操作,其他事务也只能对这个数据对象加共享锁,直到该数据对象上的所有共享锁都被释放。
分布式队列
四、zookeeper java客户端
配置中心实现原理

分布式锁实现原理
Curator组件的内置加锁功能实现方式: 彻底讲清楚ZooKeeper分布式锁的实现原理
注册中心实现原理
参考
zookeeper-step配置中心,分布式锁,分布式session代码示例
采用zookeeper的EPHEMERAL节点机制实现服务集群的陷阱